Design and bring to life your own 3D models, tailored for 3D printing.
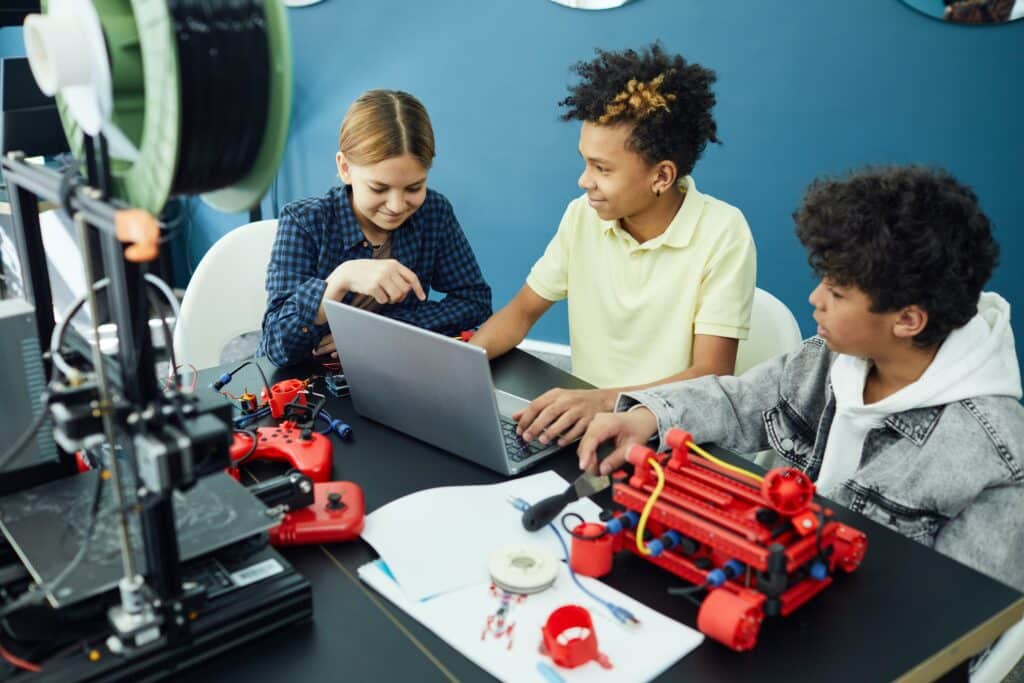

Our teachers and tutors graduated from top universities








Overview

Customized Coding Syllabus
Select the programming languages or topics that appeal to you, and we'll match you with a qualified tutor to guide you to mastery.

Adaptable Coding Sessions
Schedule lessons at your convenience, whether you desire a quick introduction or an in-depth exploration; the choice is yours.
Personalized Individual Instruction
Your learning experience is customized to your pace and preferred level of difficulty, guaranteeing steady progress without the interference of distractions or rivalry.
About Autodesk TinkerCAD
Tinkercad, developed by Autodesk, serves as an entry-level 3D modeling software that runs entirely in your web browser, eliminating the need for any downloads or installations. Its intuitive and user-friendly interface makes it ideal for beginners and younger audiences, including those with no prior experience in CAD (Computer-Aided Design).
Features and Capabilities
Constructive Solid Geometry (CSG): Tinkercad utilizes the principles of constructive solid geometry, allowing users to create complex 3D shapes by combining simpler objects. This makes it easier to visualize and manipulate designs.
Cross-Platform Accessibility: Being a web-based tool, Tinkercad allows you to access your projects from any device that has internet connectivity, providing convenience and flexibility.
Diverse Material and Color Options: Tinkercad offers a variety of pre-set materials and colors, helping you visualize what your final printed object might look like.
Built-in Lessons and Tutorials: The platform comes with a set of interactive lessons designed to get you up to speed on all the essential tools and techniques. It’s a fantastic resource for educators looking to integrate 3D modeling into their curriculum.
Codeblocks and Circuits: Beyond 3D modeling, Tinkercad also provides modules like Codeblocks for block-based programming and the Circuits environment for virtual electronics experiments, making it a multifaceted educational tool.
Export and Compatibility: The software supports exporting models in formats compatible with 3D printers, CNC machines, and even Minecraft. It seamlessly integrates with other Autodesk products and allows for easy exporting to software for more advanced editing.
Community and Sharing: Tinkercad has a vibrant online community where users can share their designs, collaborate, and seek inspiration. Its library of public designs can be a great starting point for your own projects.
Use Cases
Tinkercad is commonly used in a wide range of applications, including:
- Education: It is highly popular in schools for teaching the basics of 3D design and engineering principles.
- Prototyping: Ideal for quick prototyping of 3D models, especially for those who want to test a concept before moving it into more advanced software.
- Hobby and Personal Use: From designing custom home decor to creating unique gifts, Tinkercad is versatile enough for a wide range of personal projects.
Whether you’re a student, educator, hobbyist, or even a professional looking for a quick way to sketch out an idea, Tinkercad offers a straightforward yet powerful platform to bring your imagination to life.
Description
This course is tailored for individuals intrigued by 3D design but uncertain about where to begin. Utilizing TinkerCAD, students will fashion their unique characters or objects. It’s also suitable for children who possess a 3D printer and wish to create and print their designs instead of using pre-made ones.
What you will learn
- Decompose complex objects into more manageable parts.
- Visualize and construct objects in 3D
- Enhance 2D art skills and sketch original characters.
- Ready 3D models for printing.
- Modify existing 3D designs.
Requirements
- Ages 7 – 13
- Interested in 3D design
Resources: Student FAQs About 3D Printing
Layering is the process where a 3D printer builds up an object one layer at a time, from the bottom up. Each layer fuses to the one beneath it to form a solid object. Understanding how layering works is essential for optimizing print speed and quality.
FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) and SLA (Stereolithography) are two of the most common 3D printing technologies. FDM melts plastic filaments and extrudes it layer by layer to build an object. SLA uses a laser to solidify liquid resin in a layer-by-layer fashion. Each has its advantages and disadvantages in terms of print quality, material options, and speed.
Infill refers to the internal structure of your 3D printed object. You can adjust the infill density to make your object more solid or hollow, affecting both the print time and the amount of material used. A higher infill percentage makes the object stronger but consumes more material and takes longer to print.
Support material is additional material printed to support overhangs and complex shapes that can’t be printed in mid-air. These are usually removed post-printing. Whether or not you’ll need support depends on the geometry of the object you’re printing.
Bed leveling ensures that the printing surface is flat and aligned with the nozzle, which is critical for print quality. An unleveled bed can result in poor adhesion, irregular layers, or even a failed print. Most modern 3D printers offer some form of automatic bed leveling, but manual calibration is also common in older or budget models.
How it works
1
Request a tutor
Let us know your goals and age range. We'll figure out a plan to help get you there.
2
Match with a tutor
We'll recommend you a tutor based on your needs and goals, or you can request a specific tutor.
3
Start a free trial
Experience a free trial lesson with your new tutor and see if your learning style matches.
4
Keep it up!
If everything went well, sign up to keep going! You can choose the pacing of the lessons
Need more info?
Let's talk.
Leave your phone number, and we’ll call you back to discuss how we can help you.